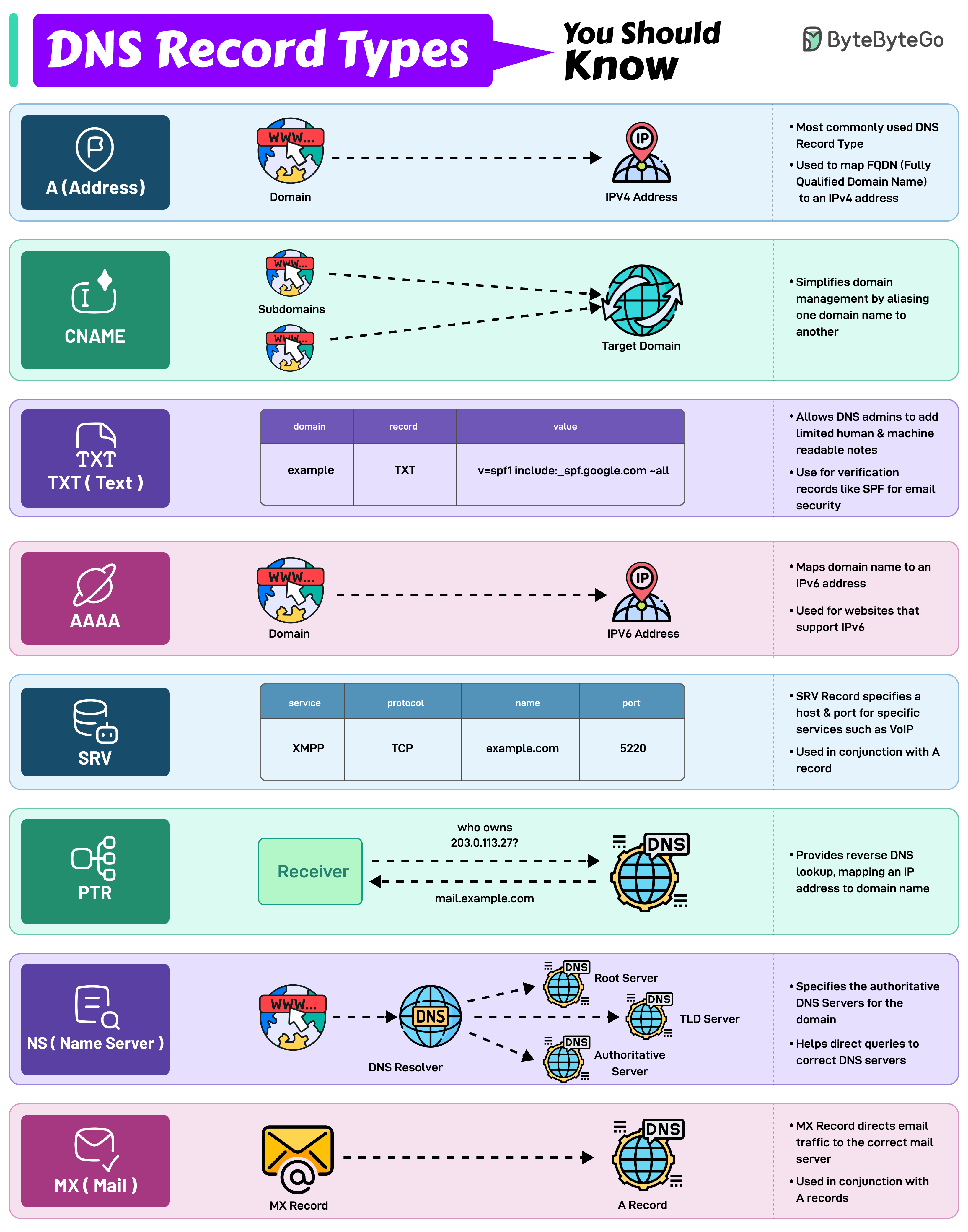
📘 DNS Record Types
Record Type | Kya Karta Hai | Use Case (Example) | Extra Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
A (Address) | Domain ko IPv4 address se map karta hai | example.com → 192.168.1.1 | Sabse common record, websites ke liye |
AAAA | Domain ko IPv6 address se map karta hai | example.com → 2606:4700::1111 | Jab website IPv6 support karti ho |
CNAME | Ek domain ko dusre domain ka alias banata hai | www.example.com → example.com | Subdomains ko simplify karne ke liye |
TXT | Human ya machine readable info store karta hai | v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com -all | Mostly verification aur SPF/DKIM ke liye |
SRV | Kisi service ke liye host + port specify karta hai | XMPP over TCP @ port 5220 | VoIP jaise protocols ke liye use hota hai |
PTR | Reverse DNS lookup karta hai (IP → Domain) | 203.0.113.277 → mail.example.com | Email server verification ke liye zaroori |
NS (Name Server) | Batata hai kaunse server domain ke liye authoritative hain | DNS resolution ke time use hota hai | TLD, root & authoritative DNS ka part |
MX (Mail Exchange) | Email traffic ko mail server pe route karta hai | MX → mail.example.com (A record ke saath) | Email system ke liye important |
DNS Record kya hota hai?
DNS records (jise zone files bhi kehte hain) aise instructions hote hain jo authoritative DNS servers mein store hote hain. Ye batate hain ki kisi domain ka kaunsa IP address hai aur us domain ke requests ko kaise handle karna hai.
Ye records ek tarah ke text files hote hain jo DNS syntax mein likhe hote hain. DNS syntax basically ek string hoti hai jo DNS server ko batati hai ki kya karna hai.
Har DNS record ka ek TTL (Time-To-Live) bhi hota hai – iska matlab hai ki DNS server us record ko kitni baar refresh karega.
Aap DNS records ko Yelp ke ek business listing jaise samajh sakte ho – jaise Yelp pe kisi business ka address, timing, services wagairah diye hote hain, waise hi DNS records domain ka data batate hain.
Har domain ke liye kuch basic DNS records hona mandatory hai, jisse log us website ko domain name se access kar sakein. Saath hi kuch optional records bhi hote hain jo extra kaam ke liye use hote hain.
Common types of DNS Records (Sabse zyada use hone wale records):
A Record: Ye batata hai domain ka IPv4 address.
AAAA Record: Ye batata hai domain ka IPv6 address (IPv4 ke jagah).
CNAME Record: Ye ek domain ya subdomain ko kisi doosre domain par forward karta hai, IP address nahi deta.
MX Record: Ye email ko sahi mail server par direct karta hai.
TXT Record: Admin text information store kar sakta hai – mostly email security ke liye use hota hai.
NS Record: Ye batata hai ki DNS entry ka name server kaunsa hai.
SOA Record: Domain ka admin info store karta hai.
SRV Record: Specific service ke liye port specify karta hai.
PTR Record: Reverse DNS lookup mein domain name deta hai.
Less common DNS Records (Kam use hone wale records):
AFSDB Record: Andrew File System ke liye clients ko other AFS cells dhoondhne mein help karta hai.
APL Record: Address prefix list – address ranges define karta hai (experimental).
CAA Record: Ye batata hai kaunse Certificate Authority domain ke liye SSL certificate issue kar sakte hain.
DNSKEY Record: DNSSEC signatures verify karne ke liye public key rakhta hai.
CDNSKEY Record: Child DNSKEY record jo parent ko diya jata hai.
CERT Record: Public key certificates store karta hai.
DCHID Record: DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) ka identifier.
DNAME Record: Domain alias banata hai (subdomains bhi redirect hoti hain).
HIP Record: IP address ke roles ko alag karta hai, mostly mobile computing mein use hota hai.
IPSECKEY Record: IPSEC security protocol ke liye key store karta hai.
LOC Record: Domain ka geographical info store karta hai (longitude, latitude).
NAPTR Record: SRV record ke saath milke URI dynamically generate karta hai.
NSEC Record: DNSSEC ka part – ye prove karta hai ki koi DNS record exist nahi karta.
RRSIG Record: DNSSEC ke hisaab se digital signatures store karta hai.
RP Record: Responsible person ka email address rakhta hai.
SSHFP Record: SSH public key fingerprints rakhta hai (Secure Shell ke liye).
✅ 1. AFSDB Record
Full Form: Andrew File System Database Record
Use: Ye record batata hai ki kisi AFS client ko kis AFS cell se connect hona chahiye.
🔹 Example: Sochiye aapke paas AFS client software hai jo kisi distributed file system se data fetch karta hai. Ab vo client DNS se poochta hai: “Bhai mujhe yeh file chahiye, kis server se milegi?”
AFSDB record batata hai ki kaunsa server ya cell responsible hai.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise aap Zomato app se food order karte ho, app batata hai kaunsa restaurant aapke location ke liye available hai. Waise hi AFSDB batata hai kaunsa AFS cell available hai.
✅ 2. APL Record
Full Form: Address Prefix List
Use: Ye experimental record hai jo address ranges define karta hai (e.g. 192.168.0.0/24).
🔹 Example: APL record ye specify karta hai ki “ye domain sirf in IP address ranges ke logon ke liye valid hai”.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise kisi society ke gate pe list hoti hai ki kaunse flats ke log allowed hain – waise hi APL batata hai kaunse IPs ko access milega.
✅ 3. CAA Record
Full Form: Certification Authority Authorization
Use: Ye batata hai ki kaunse Certificate Authorities (CA) SSL/TLS certificate issue kar sakte hain.
🔹 Example: Agar aap chahte ho ki sirf Let’s Encrypt hi aapke domain ke liye certificate issue kare, toh aap CAA record set karoge:
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise aap keh dete ho ki “meri property ka kaam sirf Anil Advocate karega, koi aur nahi”. Waise hi yeh record control karta hai SSL certificate issuance.
✅ 4. DNSKEY Record
Use: DNSSEC ka part hai – isme public key hoti hai jo DNS records ki authenticity verify karti hai.
🔹 Example: Jab user DNS query bhejta hai, DNSKEY record uss response ko digitally sign karta hai taaki ensure ho ki data tamper nahi hua.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise courier ka packet seal hota hai – DNSKEY us seal ke jaisa hai.
✅ 5. CDNSKEY Record
Use: Ye DNSKEY ka child version hai, jo parent zone ko diya jata hai taaki DNSSEC trust chain maintain ho.
🔹 Example: Subdomain login.example.com apna CDNSKEY example.com ko deta hai jisse verify kiya ja sake.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise birth certificate child ka hota hai, but family register parent ke paas hota hai.
✅ 6. CERT Record
Use: Ye record SSL/TLS ya kisi bhi type ka public key certificate store karta hai.
🔹 Example: Agar aapka server self-signed certificate use karta hai toh aap uska data CERT record me rakh sakte ho.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise college ID card pe student ka name, roll no. hota hai – waise hi CERT record digital ID deta hai.
✅ 7. DCHID Record
Full Form: DHCP Identifier
Use: DHCP ke clients ke identification ke liye use hota hai.
🔹 Example: Jab koi device IP mangta hai DHCP server se, to server DCHID record check karta hai device verify karne ke liye.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise building ka guard kisi visitor ka ID proof mangta hai before entry.
✅ 8. DNAME Record
Use: Ek domain ko dusre domain ka alias banata hai – aur subdomains bhi redirect karta hai.
🔹 Example:
Toh blog.website.net bhi blog.example.com pe chala jaayega.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise kisi company ne naya naam le liya – purane naam ke sab documents naye naam pe redirect ho jaate hain.
✅ 9. HIP Record
Full Form: Host Identity Protocol
Use: IP address ke identity aur location role ko separate karta hai – mainly mobile devices ke liye.
🔹 Example: Agar ek mobile device location change karta hai but identity same rakhta hai, to HIP record help karta hai.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise SIM card change nahi hua, par location change hoti rahi.
✅ 10. IPSECKEY Record
Use: IPSEC (Internet Protocol Security) ka part – end-to-end encrypted communication ke liye public key deta hai.
🔹 Example: VPN tunnels establish karte time IPSECKEY use hota hai.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise two people secret codes exchange karte hain to talk privately.
✅ 11. LOC Record
Use: Kisi domain ka geographical location define karta hai (longitude, latitude).
🔹 Example:
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise Google Maps pe kisi jagah ka pin drop karna.
✅ 12. NAPTR Record
Use: URI dynamically generate karta hai SRV record ke saath using regular expressions.
🔹 Example: SIP (VoIP) call ke liye dynamic address banane me help karta hai.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise contact form me data bharte hi automatic email ya link generate hota hai.
✅ 13. NSEC Record
Use: DNSSEC ka part – prove karta hai ki koi DNS record exist nahi karta.
🔹 Example: Agar koi hacker fake DNS record dalta hai, NSEC bata deta hai ki vo record kabhi tha hi nahi.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise ek register me naam nahi milne par proof milta hai ki banda wahan kabhi tha hi nahi.
✅ 14. RRSIG Record
Use: DNSSEC digital signatures ko verify karne ke liye use hota hai – authenticity ke liye.
🔹 Example: Jab user DNS response receive karta hai, RRSIG check karta hai ki response tampered nahi hua.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise koi contract document pe authorized signature hona.
✅ 15. RP Record
Full Form: Responsible Person
Use: Domain ka responsible admin ka email address batata hai.
🔹 Example:
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise kisi apartment ka secretary ka contact board pe likha ho emergency ke liye.
✅ 16. SSHFP Record
Use: SSH ke fingerprints store karta hai taaki secure server connection ban sake.
🔹 Example: Jab aap kisi server pe SSH karte ho, toh SSHFP se verify hota hai ki server trusted hai ya nahi.
🧠 Real Life Samjho: Jaise kisi ke signature verify karne se pata chalta hai ki samne wala asli hai ya nahi.
