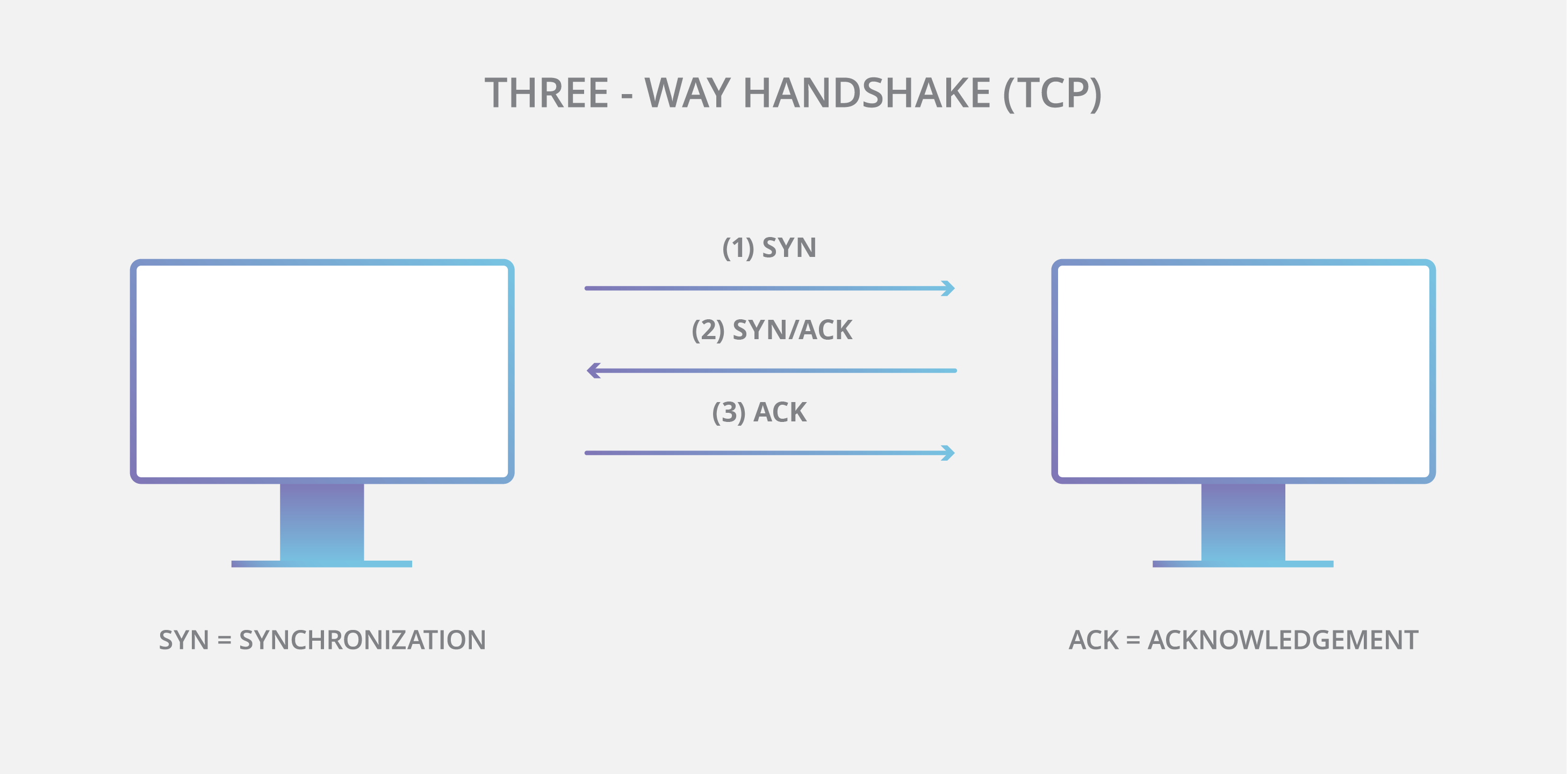
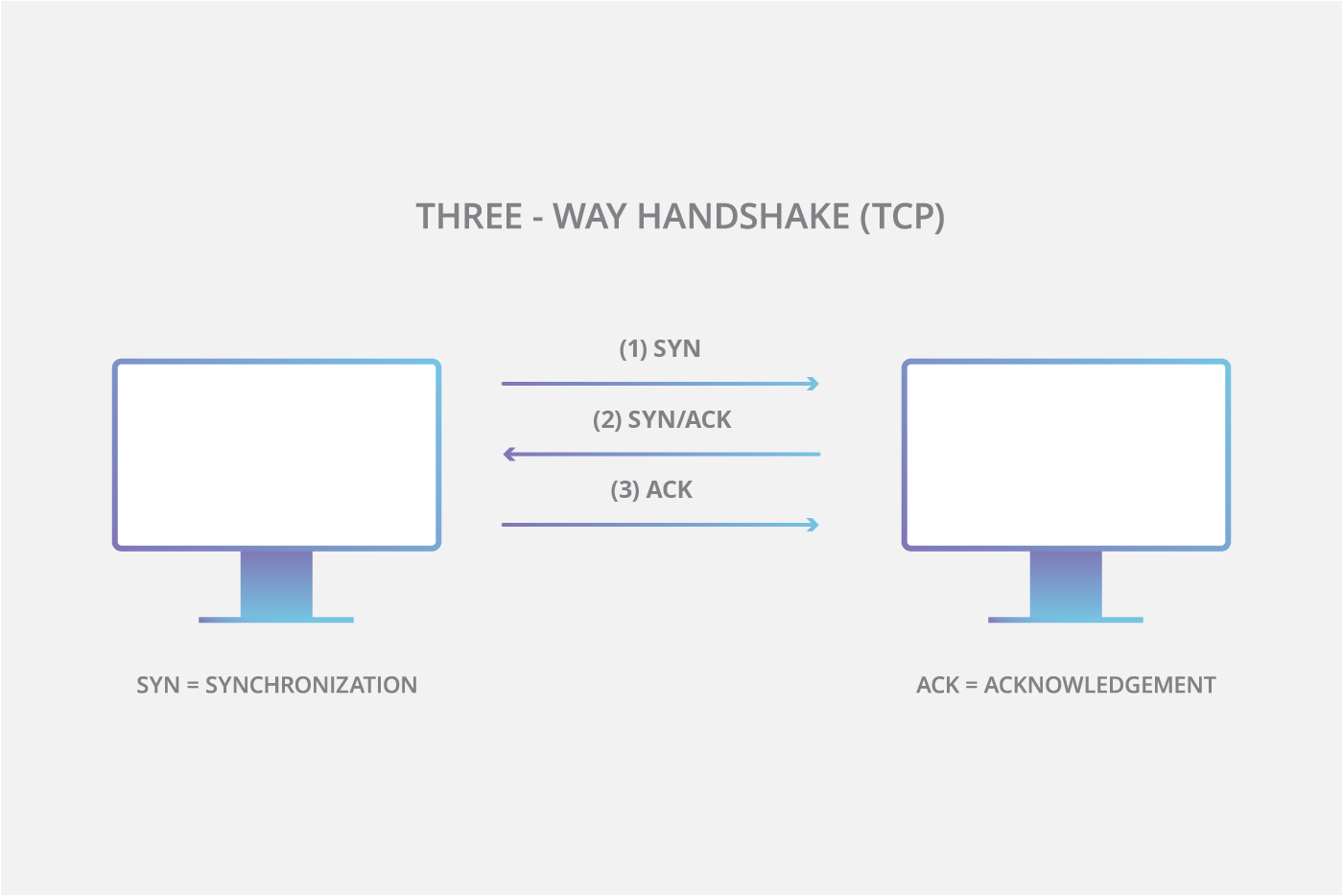
Denial-of-service create karne ke liye, attacker TCP handshake ke process ka misuse karta hai. Jab server initial SYN packet receive karta hai, to wo SYN/ACK packet bhej kar final ACK ka wait karta hai. Ab ye attack kaise kaam karta hai, ye dekhiye:
Attacker target server ko bahut saare SYN packets bhejta hai, aksar spoofed (fake) IP addresses ke saath.
Server har SYN packet ka reply SYN/ACK se karta hai aur har connection ke liye ek port temporarily open rakhta hai, ACK ka wait karte hue.
Lekin wo final ACK kabhi nahi aata. Attacker continuously naye SYN packets bhejta rehta hai.
Server ke jitne bhi available ports hote hain, wo sab temporary open ho jaate hain, aur har port kuch time tak busy bana rehta hai.
Jab saare ports use ho jaate hain, server naye genuine connections ko accept nahi kar pata, aur system slow ya completely unresponsive ho jaata hai.
Is tarah se SYN flood attack server ko crash kiya bina hi use unavailable bana deta hai.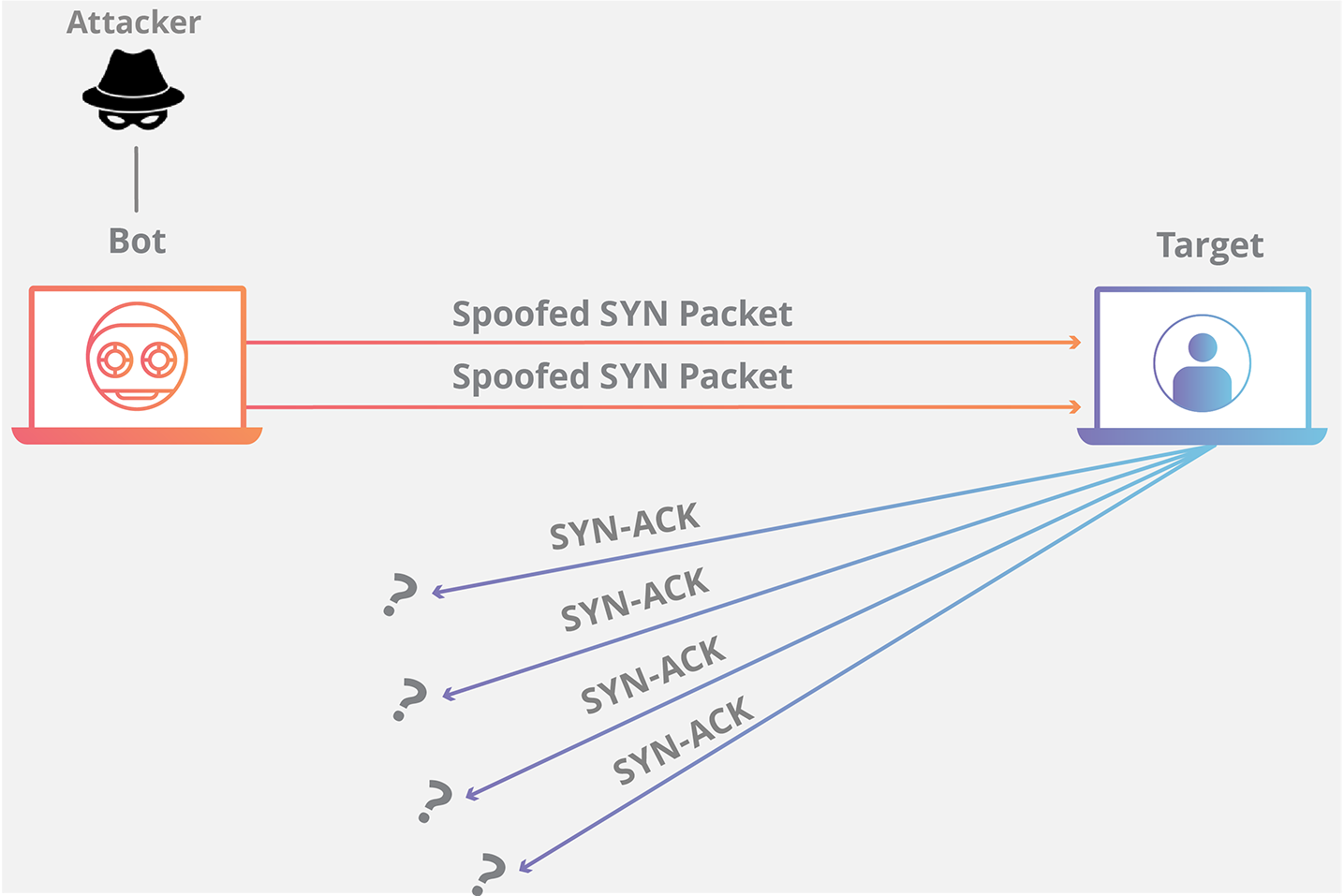
Networking mein, jab server ek connection open chhod deta hai lekin saamne wali machine response nahi karti, to is connection ko half-open kaha jaata hai. Is type ke DDoS attack mein, targeted server baar-baar open connections chhodta rehta hai aur har connection ke timeout hone ka wait karta hai jab tak ports dobara available na ho jaayein. Isi wajah se is attack ko “half-open attack” bhi kaha jaata hai.
SYN flood 3 tariko se ho sakta hai:
1. Direct attack:
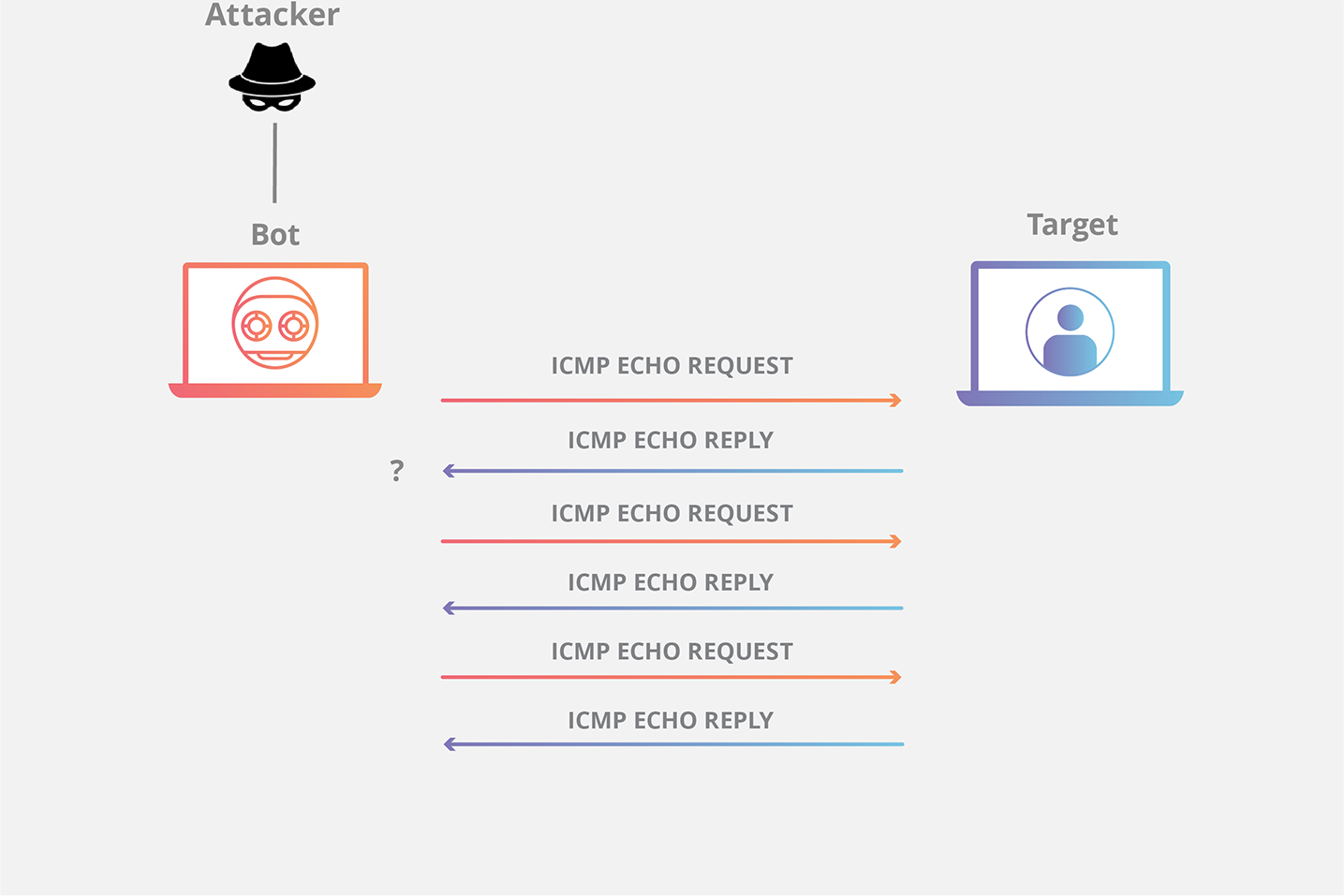
Jab SYN flood mein IP address spoof nahi kiya jaata, to usse direct attack kehte hain. Ismein attacker apna real IP address use karta hai, jisse uska track hona aasaan ho jaata hai. Attack karne ke liye, attacker apni machine ko server ke SYN-ACK packets ka response dene se rokta hai. Ye kaam firewall rules ke through kiya ja sakta hai jo outgoing SYN packets ke alawa sabko block kar dete hain ya phir incoming SYN-ACK packets ko filter kar dete hain. Ye method zyada use nahi hota, kyunki iska countermeasure simple hai – attacker ke IP ko block kar do. Agar attacker botnet (jaise Mirai botnet) use kar raha hai, to IP mask karna uske liye zaroori nahi hota.
2. Spoofed Attack:
Malicious user har SYN packet ke IP address ko spoof kar sakta hai jisse uski identity trace karna mushkil ho jaaye. Spoofed packets traceable ho sakte hain, lekin ye kaafi mushkil process hai – especially jab tak ISPs help na karein.
3. Distributed Attack (DDoS):
Agar attacker botnet (jaise Mirai) ka use karta hai, to source ka track karna aur bhi mushkil ho jaata hai. Har bot bhi spoofed IPs se packets bhej sakta hai, jisse detection aur bhi tough ho jaata hai. Mirai jaise botnet ke case mein attacker infected devices ke IP ko mask karne ki chinta nahi karta.
SYN flood attack kyun effective hai?
SYN flood attack se attacker kam traffic me bhi denial-of-service create kar sakta hai, dusre DDoS attacks ke mukable. Volumetric attacks network ko saturate karte hain, lekin SYN attacks sirf target system ke backlog size se zyada hone chahiye. Agar attacker ko backlog size aur connection timeout ka duration pata chal jaaye, to wo minimum traffic me system ko disable kar sakta hai.
SYN flood attack se kaise bacha jaaye (mitigation)?
1. Backlog queue badhaana:
Har system me ek limit hoti hai ki kitne half-open connections allow honge. Is limit ko badhaane se zyada SYN packets handle kiye ja sakte hain. Lekin memory resources bhi zyada chahiye honge. Agar memory kam pad gayi, to performance degrade ho sakti hai – lekin ye denial-of-service se phir bhi behtar hai.
2. Oldest Half-Open connection ko recycle karna:
Backlog full hone par, sabse purane half-open connection ko overwrite karna. Ye tabhi effective hai jab genuine connections attacker ke packets se pehle complete ho jaayein. High-volume attacks me ye approach fail ho sakti hai.
3. SYN cookies:
Isme server ek cookie create karta hai. Server SYN-ACK bhejta hai lekin backlog me entry nahi rakhta – yaani memory free rehti hai. Agar client ACK bhejta hai (yaani connection genuine hai), to server backlog entry reconstruct kar leta hai. Thoda connection data lose hota hai, lekin attack ke comparison me ye approach better hai.
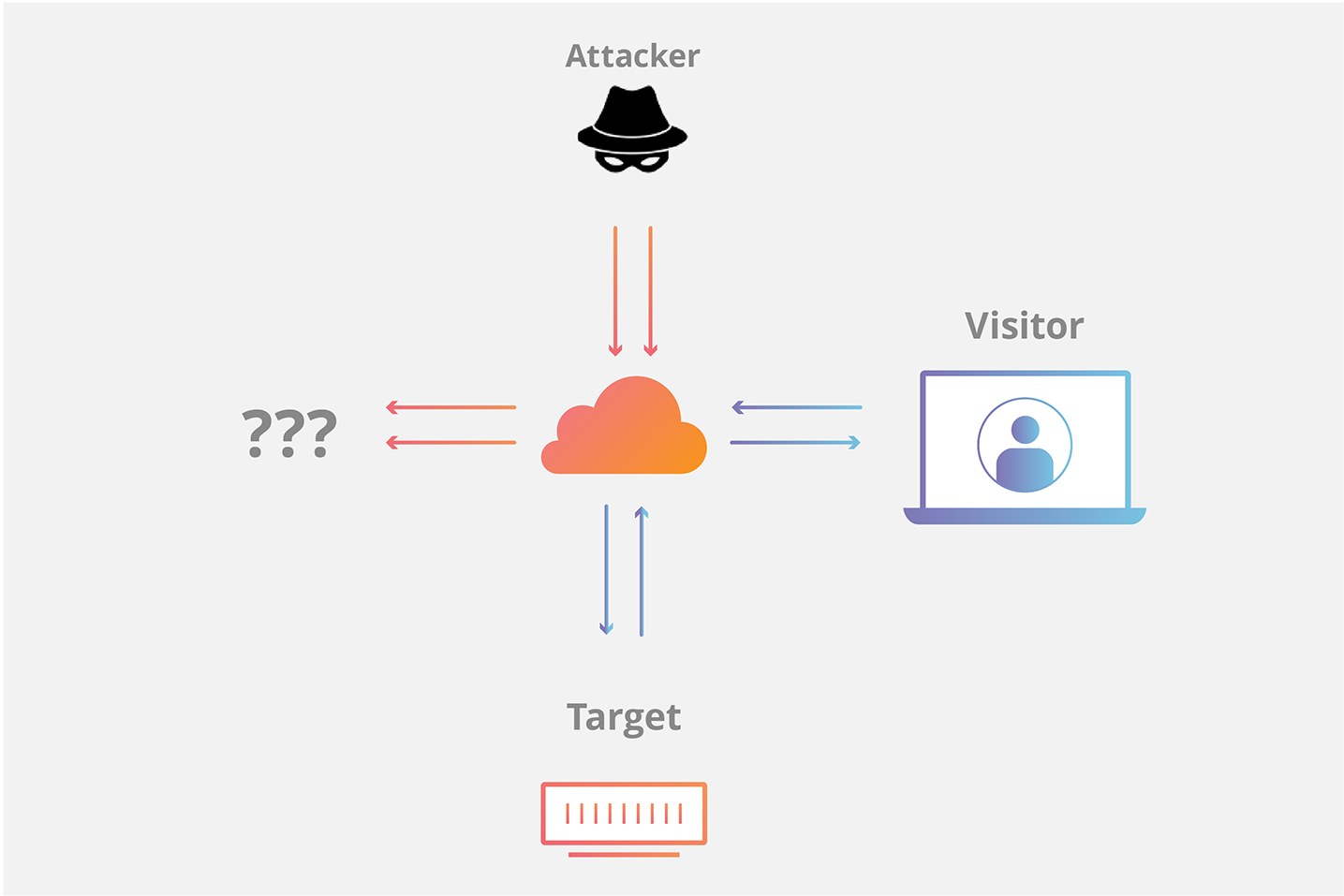
Cloudflare kaise SYN flood attacks se bachata hai?
Cloudflare is attack ko rokta hai by acting as a middle layer. Jab initial SYN request aati hai, Cloudflare handshake process ko apne cloud par handle karta hai aur server tak tab tak request nahi jaane deta jab tak handshake complete nahi ho jaata. Isse bogus SYN packets ka load Cloudflare par shift ho jaata hai, na ki target server par. Ye kaam Cloudflare ke Anycast network ke zariye hota hai.