Unit – 5: Data Communication and Computer Network
Contents:
Introduction to Communication System
Modes of Communication
Introduction to Computer Network
LAN Topologies
Transmission Media
Network Devices
OSI Reference Model
Communication Protocols
Centralized vs Distributed System
Introduction to Data Communication
Data Communication ka matlab hota hai do devices ke beech data ka exchange karna, kisi transmission medium (jaise wire cable) ke through.
Data communication tabhi possible hoti hai jab dono communicating devices ek communication system ka part ho. Ye system hardware (jaise physical devices) aur software (jaise programs) ka combination hota hai.
Fundamental Characteristics
Ek data communication system ki effectiveness 4 basic characteristics pe depend karti hai:
Delivery, Accuracy, Timeliness, aur Jitter
1. Delivery
System ko data sahi jagah (correct destination) tak pahunchana chahiye. Data ko sirf ussi device ya user tak pahunchna chahiye jiske liye wo intended hai — kisi aur ko nahi.
2. Accuracy
System ko data bilkul sahi (accurately) deliver karna chahiye. Agar transmission ke dauraan data galat ho gaya aur wo correct nahi hua, to wo data bekaar ho jata hai.
3. Timeliness
System ko data time pe deliver karna chahiye. Agar data late pahunchta hai to wo kaam ka nahi hota. Video aur audio ke case mein, timely delivery ka matlab hai: data ko produce hote hi turant deliver karna — same order mein, bina kisi significant delay ke. Is type ki delivery ko real-time transmission kehte hain.
4. Jitter
Jitter ka matlab hai packets ke arrival time mein variation. Yaani audio ya video packets jab uneven delay se pahunchte hain, to isse jitter kehte hain.
Components of Data Communication
Ek data communication system ke 5 main components hote hain:
1. Message
Message woh information ya data hoti hai jo communicate ki jaani hai. Common types of information mein aate hain: text, numbers, pictures, audio, aur video.
2. Sender
Sender woh device hoti hai jo data message bhejti hai. Ye ek computer, workstation, telephone handset, video camera ya koi aur device ho sakti hai.
3. Receiver
Receiver woh device hoti hai jo message ko receive karti hai. Ye bhi computer, workstation, telephone handset, TV ya koi aur device ho sakti hai.
4. Transmission Medium
Transmission medium woh physical path hota hai jiske through message sender se receiver tak jata hai. Kuch common examples hain:
twisted-pair wire, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, aur radio waves.
5. Protocol
Protocol ek set of rules hota hai jo data communication ko control karta hai. Ye dono communicating devices ke beech ek agreement hota hai jisme tay hota hai ki data kaise send aur receive kiya jayega.
Modes of Data Communication
Do devices ke beech communication 3 modes mein ho sakti hai:
👉 Simplex, Half-Duplex, aur Full-Duplex
1. Simplex Mode
Simplex mode mein communication sirf ek direction mein hoti hai — jaise ek one-way street.
Ismein sirf ek device data bhej sakti hai, aur doosri sirf receive kar sakti hai.
Examples:
Keyboard → sirf input deta hai
Monitor → sirf output show karta hai
Simplex mode mein channel ki poori capacity ek hi direction mein data bhejne ke liye use hoti hai.
2. Half-Duplex Mode
Half-duplex mode mein dono devices transmit aur receive kar sakti hain, lekin ek time pe sirf ek hi kaam karegi — ya to send ya receive.
Jab ek device data bhej rahi hoti hai, to doosri sirf receive karti hai — aur vice versa.
Examples:
Walkie-talkie
CB radio
Yeh mode tab use hota hai jab ek waqt mein dono taraf se communication ki zarurat nahi hoti, aur channel ki poori capacity ek direction mein use ki ja sakti hai.
3. Full-Duplex Mode
Full-duplex mode mein dono devices ek saath transmit aur receive kar sakti hain — jaise two-way traffic jahan dono directions mein gaadiyan chal rahi hoti hain.
Is mode mein, signals ek direction mein jaate hue link ki capacity ko share karte hain doosri direction ke signals ke saath.
Example:
Telephone call → Dono log ek saath baat karte hain aur sunte hain
Full-duplex mode tab use hota hai jab har waqt dono directions mein communication chahiye hoti hai. Lekin ismein channel ki capacity dono directions ke beech divide hoti hai.
Computer Network
Computer Network ek group hota hai computers aur other hardware devices ka jo ek dusre se communication channels ke through connected hote hain. Iska main purpose hota hai communication aur resource sharing allow karna multiple users ke beech.
Network Criteria
Ek achhe network ko kuch basic criteria meet karne chahiye. Sabse important criteria hain:
👉 Performance, Reliability, aur Security
1. Performance
Performance ko alag-alag tareekon se measure kiya ja sakta hai, jaise:
Transit Time: Ek message ko ek device se dusri device tak pahunchne mein lagne wala time.
Response Time: Jab ek inquiry bheji jaye aur uska response milne mein lagne wala time.
Network ki performance depend karti hai:
Users ki sankhya pe
Transmission medium ke type pe
Connected hardware ki capability pe
Software ki efficiency pe
2. Reliability
Network ki reliability measure hoti hai:
Kitni baar failure hota hai (frequency of failure)
Failure ke baad kitni jaldi link recover hota hai
Catastrophe (jaise natural disaster ya crash) ke samay network kitna robust hai
3. Security
Security ka matlab hai:
Unauthorized access se data ki protection
Data corruption ya damage se bachav
Policies aur procedures ka hona taaki breach ya data loss ke baad recovery ho sake
Types of Connections
Network mein do tarah ke connections ho sakte hain:
1. Point-to-Point
Point-to-point connection mein sirf do devices ke beech ek dedicated link hota hai.
Is link ki poori capacity sirf inhi do devices ke beech data transmission ke liye hoti hai.
2. Multipoint (ya Multidrop)
Multipoint connection mein ek hi link ko do se zyada devices share karte hain.
Ismein channel ki capacity ya to spatially (ek saath) ya temporally (turn by turn) share hoti hai.
Spatially Shared: Agar multiple devices ek saath link use kar sakte hain.
Time-Shared: Agar devices ko turn-wise link use karna padta hai.
Types of Computer Network
Computer networks ko 4 alag-alag criteria ke basis pe different types mein divide kiya ja sakta hai:
1. Geographic Spread of Nodes and Hosts
Network ka type uski physical distance pe depend karta hai — yaani ki devices (hosts) kitni door tak connected hain.
LAN (Local Area Network):
Jab hosts ek chhoti physical area (jaise ek building ya campus) ke andar connected hote hain.
Example: Office ka internal network, college campus network, etc.MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
Jab network poore sheher ya kuch 100 kilometers tak spread hota hai.
Example: City-wide cable TV network.WAN (Wide Area Network):
Jab network desh, continent, ya pure globe mein spread ho.
Example: Internet.
2. Access Restrictions
Network kis type ke users ke liye accessible hai — is base pe bhi types hote hain:
Private Network:
Sirf ek particular organization ke use ke liye hota hai.
Example: Banks, hospitals, airlines ka internal network.Public Network:
General public ke liye available hota hai (kahi baar registration aur charges lagte hain).
Example: Internet.
3. Communication Model Employed by the Nodes
Nodes ke beech communication model kaise kaam karta hai:
Point-to-Point Model:
Do specific devices ke beech direct link hota hai.Broadcast Model:
Ek device ka message sabhi devices tak broadcast hota hai (jaise TV signals ya Wi-Fi).
4. Switching Model Employed by the Nodes
Point-to-point model mein data ko transfer karne ke liye 2 switching techniques hoti hain:
Circuit Switching:
Ek dedicated path set hota hai sender (A) se receiver (B) tak.
Example: Traditional telephone lines.Packet Switching:
Data ko chhote packets mein tod diya jata hai.
Har packet intermediate nodes ke through travel karta hai.
Har node temporarily packet ko store karta hai jab tak receiver ready na ho.
LAN Topologies
Broadcast LAN ke liye alag-alag topologies possible hoti hain jaise ki bus, ring, ya mesh topology.
1. Bus Topology
Bus topology ek multipoint connection hoti hai. Ek lambi si cable hoti hai jo backbone ka kaam karti hai, aur yeh backbone sabhi devices ko network mein connect karti hai. Har node ko is bus cable se drop lines aur taps ke zariye connect kiya jata hai. Jab signal is backbone ke through travel karta hai, toh uski kuch energy heat mein convert ho jati hai. Is wajah se signal dheere-dheere weak hota jata hai jaise-jaise wo aage badhta hai.
Is wajah se bus topology mein limited number of taps hote hain aur taps ke beech ki distance bhi ek limit tak hi possible hoti hai.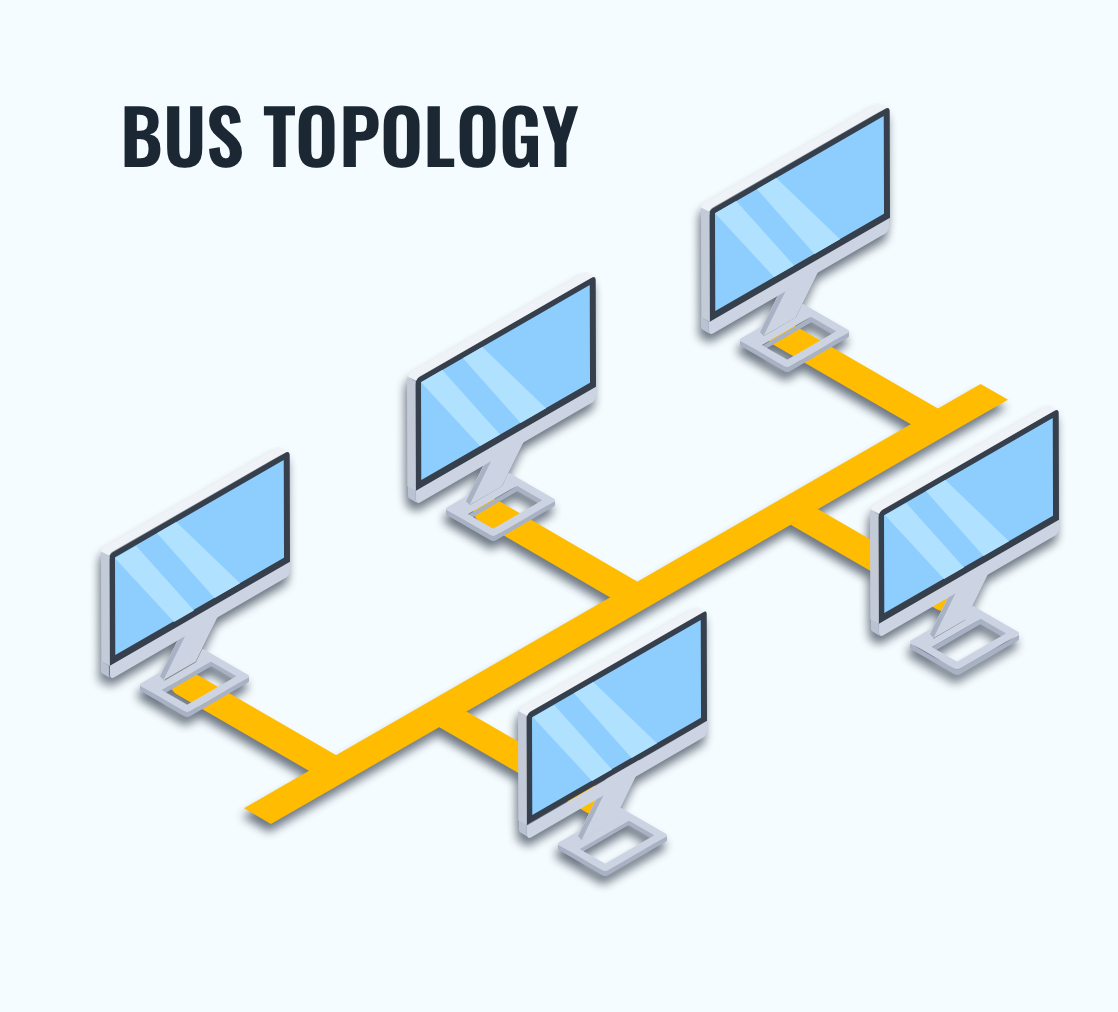
2. Ring Topology
Ring topology mein har device ka ek dedicated point-to-point connection hota hai sirf apne dono side ke do devices ke saath. Ek signal ring ke around sirf ek direction mein travel karta hai – ek device se doosri device tak – jab tak wo apne destination tak nahi pahuchta.
Ring mein har device ke andar ek repeater hota hai. Jab kisi device ko koi aisa signal milta hai jo uske liye nahi hai, toh uska repeater us signal ke bits ko regenerate karta hai aur us signal ko aage pass kar deta hai.

3. Star Topology
Star topology mein har device ka ek dedicated point-to-point link hota hai ek central controller ke saath, jise usually hub kaha jata hai. Devices ek dusre ke saath directly connected nahi hote. Mesh topology ke opposite, star topology mein devices ke beech direct traffic allowed nahi hota.
Is topology mein controller exchange ka kaam karta hai: agar ek device kisi doosre device ko data bhejna chahta hai, toh pehle wo data controller ko bhejta hai, fir controller us data ko destination device tak forward karta hai.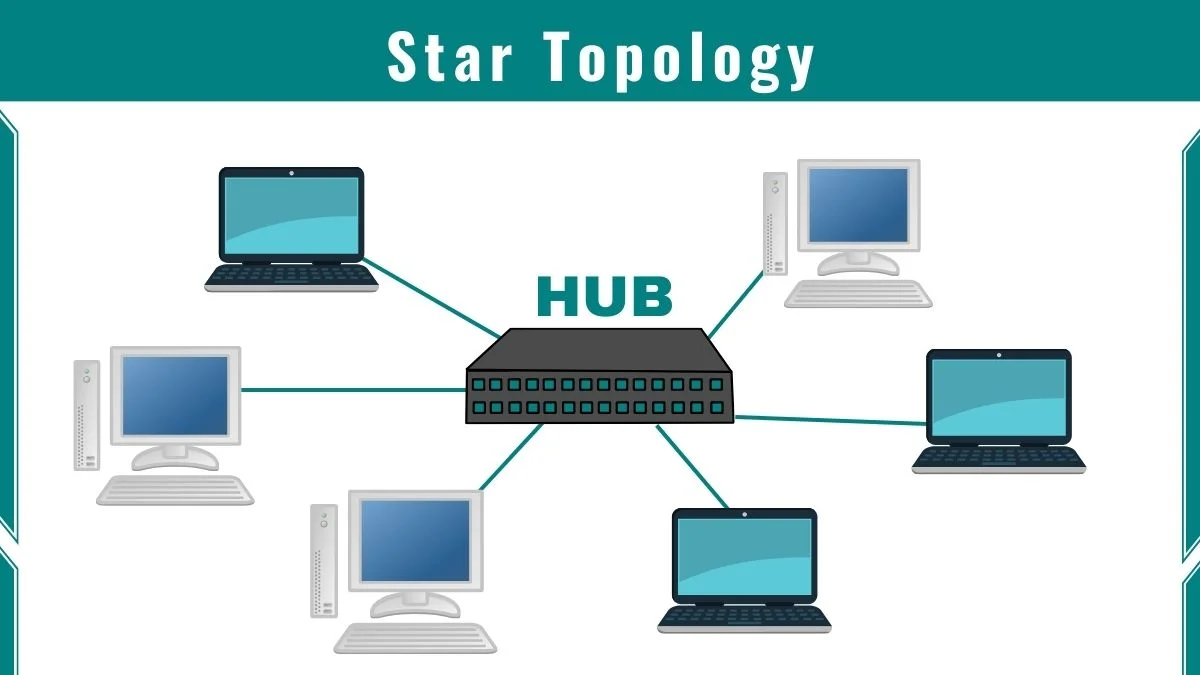
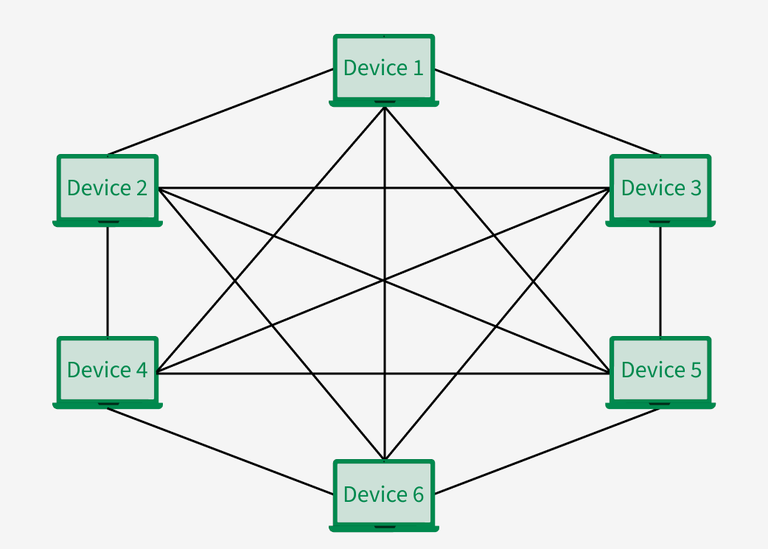
4. Mesh Topology
Mesh topology mein har device ka ek dedicated point-to-point link hota hai har doosre device ke saath. Yahan “dedicated” ka matlab hai ki har link sirf un do devices ke beech ka traffic carry karta hai jo us link se connected hain — koi aur device us link ka use nahi karta.
Iska fayda yeh hota hai ki communication fast aur secure hota hai, kyunki har pair ke beech ek direct connection hota hai. Lekin ismein bohot zyada cabling lagti hai, especially jab network mein devices zyada ho jaate hain.
Transmission Media
Transmission medium ka matlab hota hai koi bhi cheez jo source se destination tak information carry kar sake. Ye medium generally free space, metallic cable, ya fiber-optic cable ho sakta hai.
Jo information bheji ja rahi hoti hai, wo usually signal ke form mein hoti hai — jo kisi data ka converted version hota hai.
🔹 Guided Media (Physical Medium ke through signal jaata hai)
Isme signal ek physical path ke andar travel karta hai — jaise cable. Guided media mein teen major types hote hain:
1. Twisted-Pair Cable
Is cable mein 2 copper wires hote hain, jo plastic insulation ke saath twist kiye hote hain.
Ek wire signal bhejne ke liye hota hai, doosra ground reference ke liye.
Twisting karne se interference aur crosstalk (ek signal ka doosre mein ghus jaana) kam ho jaata hai.
Example: Telephone lines mein yeh cable use hoti hai voice aur data ke liye.
2. Coaxial Cable
Coax cable high-frequency signals ko carry karta hai.
Isme ek central copper wire hoti hai, jise insulating material se cover kiya gaya hota hai.
Uske baahar ek metallic shield hoti hai (foil ya braid).
Better shielding deta hai, isliye TV cables, broadband internet mein use hota hai.
3. Fiber-Optic Cable
Yeh cable glass ya plastic se banti hai, aur signal ko light ke form mein transmit karti hai.
Light signals reflection ke through ek jagah se doosri jagah tak jaate hain.
Cable mein core (glass/plastic) hota hai jise cladding surround karti hai.
Cladding ki density kam hoti hai, jisse light reflect hoti hai instead of refracting (bikharti nahi).
✅ Advantages of Fiber-Optic Cable:
High bandwidth – Bohot zyada data transfer kar sakta hai.
Low signal loss – 50 km tak signal bina regenerate kiye ja sakta hai.
No electromagnetic interference – Light par noise ka effect nahi hota.
Corrosion-resistant – Glass copper se zyada resistant hota hai.
Lightweight – Copper cables ke comparison mein halka.
Secure – Tapping (data chura lena) mushkil hota hai.
❌ Disadvantages:
Installation aur maintenance thoda mushkil hota hai.
Unidirectional – Ek direction mein hi light ja sakti hai. Dono taraf se communication ke liye do fibers chahiye hote hain.
🔹 Unguided Media (Wireless)
Isme signal kisi physical wire ke bina travel karta hai. Isse hum wireless communication bhi kehte hain.
Signals free space mein travel karte hain.
Koi bhi device jo signal receive kar sakta hai, wo isse access kar sakta hai.
Wireless communication mein signal teen tariko se travel kar sakta hai:
Ground Propagation – Signal ground ke close travel karta hai.
Sky Propagation – Signal atmosphere mein reflect hota hai aur door tak jaata hai.
Line-of-Sight Propagation – Signal straight line mein ek antenna se doosre antenna tak jaata hai (e.g., satellite communication).
Network Device
Repeaters
Repeater ek aisa device hai jo sirf physical layer mein kaam karta hai. Network ke andar signals jo information carry karte hain, ek fixed distance tak travel kar sakte hain. Uske baad signal weak ho jata hai (attenuation) jisse data ki integrity kharab ho sakti hai. Repeater signal ko receive karta hai aur jab signal bahut weak ya corrupt hone lagta hai, to wo original bit pattern ko regenerate kar deta hai. Repeater actually do alag LANs ko nahi jodta, balki ek hi LAN ke do segments ko connect karta hai.Bridges ya Link Layer Switches
Bridge ya Link Layer Switch (ya sirf Switch) dono physical aur data link layer mein kaam karta hai. Physical layer device ke roop mein ye signal ko regenerate karta hai. Data link layer device ke roop mein, bridge frame ke andar physical (MAC) addresses (source aur destination) check karta hai. Bridge ke paas filtering ki ability hoti hai. Bridge ke paas ek table hota hai jo addresses ko ports ke saath map karta hai.Hubs
Hub bhi sirf physical layer mein kaam karta hai. Ye basically stations ko physical star topology mein connect karne ke liye use hota hai. Hub ka main nuksaan ye hai ki ye data ko sabhi connected devices ko broadcast kar deta hai. Is wajah se data collision aur corruption ke chances zyada ho jate hain hubs mein.Routers
Router ek three-layer device hai jo packets ko unke logical addresses ke basis pe route karta hai (host-to-host addressing). Router normally LANs aur WANs ko Internet mein connect karta hai aur iska apna routing table hota hai jisse routing decisions liye jate hain. Routing tables dynamic hote hain aur routing protocols ke zariye update hote hain.
Router aur repeater ya switch ke beech teen bade differences hain:
Router ke har interface ke paas physical aur logical dono addresses hote hain.
Router sirf un packets pe kaam karta hai jinke link layer destination address us interface ke address se match karte hain jahan packet aaya ho.
Router packet forward karte waqt link layer address ko badal deta hai.
Gateway
Gateway normally ek computer hota hai jo Internet ke paanch layers ya OSI model ke saat layers mein kaam karta hai. Gateway ek application message leta hai, use read karta hai aur interpret karta hai. Matlab ye do alag internetworks ko connect karne ke liye use hota hai jo alag-alag models use karte hain.
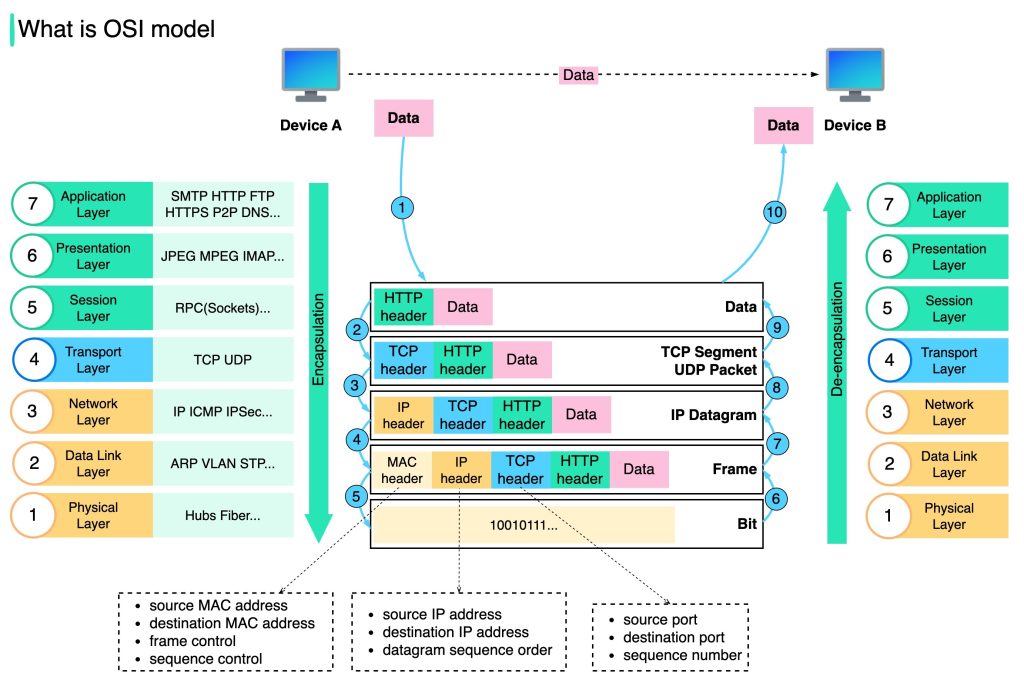
OSI Reference Model
Is model ko ISO-OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Reference Model isliye kaha jata hai kyunki ye open systems ko connect karne se related hai — matlab aise systems jo doosre systems ke saath communication ke liye open hote hain.
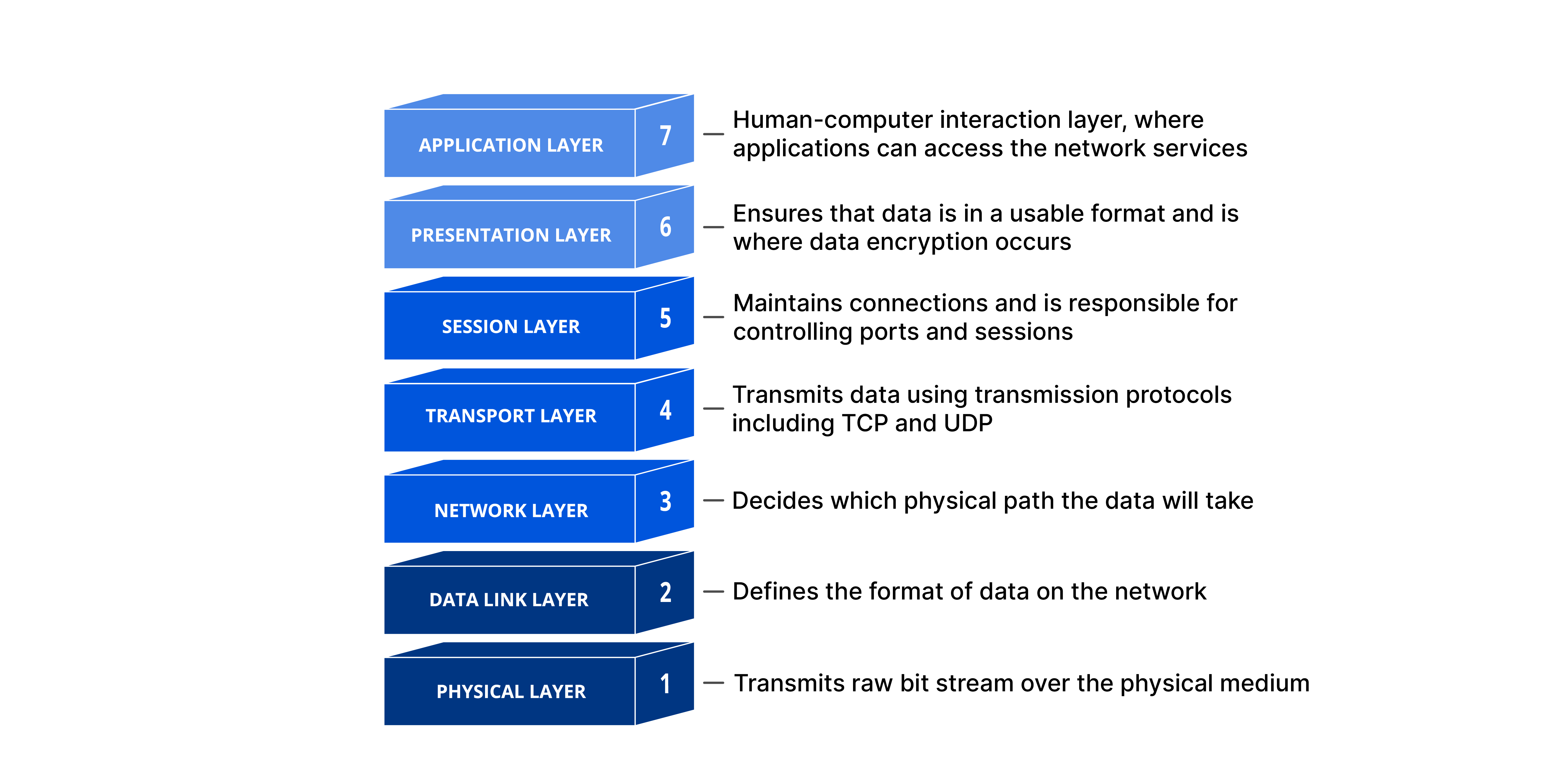
OSI model ek layered framework hai jo network systems ke design ke liye banaya gaya hai aur jo har tarah ke computer systems ke beech communication allow karta hai. Isme 7 alag-alag but related layers hoti hain, jismein se har ek layer network ke through information transfer karne ke process ka ek part define karti hai.
OSI model ke 7 layers hain:
Physical Layer (Layer 1)
Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
Network Layer (Layer 3)
Transport Layer (Layer 4)
Session Layer (Layer 5)
Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
Application Layer (Layer 7)
Jab message A se B tak travel karta hai, toh wo kai intermediate nodes se guzarta hai. Ye intermediate nodes zyada tar OSI model ke pehle 3 layers mein hi kaam karte hain.
Physical Layer
Physical layer wo layer hai jo bit stream ko physical medium ke through carry karne ke liye required functions ko coordinate karti hai. Ye mechanical aur electrical specifications ko handle karti hai jo interface aur transmission medium ke liye zaroori hain. Saath hi, ye define karti hai wo procedures aur functions jo physical devices aur interfaces ko transmission ke liye perform karne hote hain.
Data Link Layer
Data Link Layer physical layer ko ek reliable link mein convert karti hai. Ye physical layer ko upper layer (network layer) ke liye error-free banati hai.
Data Link Layer ke kuch important kaam hain:
Framing: Ye layer bits ke stream ko manageable data units mein divide karti hai, jise frames kehte hain.
Physical Addressing: Devices ko identify karne ke liye physical addresses ka use karti hai.
Flow Control: Agar receiver data ko utni speed se accept nahi kar pata jitni speed se sender data bhej raha hai, to flow control lagakar receiver ko overload hone se bachati hai.
Error Control: Data Link Layer physical layer ko reliable banati hai. Ye damaged ya lost frames ko detect karke retransmit karti hai. Duplicate frames ko bhi recognize karti hai. Error control usually frame ke end mein added trailer ke through hota hai.
Access Control: Jab ek link par do ya zyada devices connected hote hain, to data link layer protocols decide karte hain ki kis device ke paas link ka control kis waqt hai.
Network Layer
Network layer ki zimmedari hoti hai source se destination tak packet ko deliver karna, jo kai networks (links) ke through ho sakta hai. Jabki data link layer packet ko sirf ek hi network (link) ke andar do systems ke beech deliver karti hai, network layer ensure karti hai ki har packet apne origin point se lekar apni final destination tak pahunch jaye.
Network layer ke kuch aur important responsibilities hain:
Logical addressing: Data link layer physical addressing local level pe handle karti hai. Lekin jab packet network boundary cross karta hai, toh hume ek alag addressing system chahiye hota hai taaki source aur destination systems ko clearly identify kiya ja sake. Network layer upper layer se packet lene ke baad usme header add karti hai, jisme sender aur receiver ke logical addresses hote hain.
Routing: Jab alag-alag independent networks ya links ko jod kar internetworks (network of networks) ya bade network banaye jate hain, toh connecting devices (jaise routers ya switches) packets ko unki final destination tak route ya switch karte hain. Ye routing ka kaam network layer ka ek important function hai.
Transport Layer
Transport layer ki zimmedari hoti hai process-to-process delivery of poora message ka. Process matlab ek application program jo host pe chal raha hota hai. Jabki network layer har individual packet ko source se destination tak deliver karta hai bina ye dekhe ki packets ek hi message ke hain ya nahi, transport layer ensure karti hai ki pura message intact aur sahi order mein aaye, jisme error control aur flow control dono shamil hain.
Transport layer ke kuch aur functions hain:
Connection control: Transport layer connectionless bhi ho sakti hai ya connection-oriented bhi.
Flow control: Data link layer ki tarah, transport layer bhi flow control ke liye responsible hai, lekin yeh control end-to-end hota hai na ki sirf ek single link par.
Error control: Data link layer ki tarah, transport layer bhi error control karti hai, lekin yeh process-to-process level par hota hai, na ki ek single link pe. Sending transport layer ensure karti hai ki poora message receiving transport layer tak bina kisi error (damage, loss, ya duplication) ke pahunch jaye. Error correction zyada tar retransmission ke zariye hoti hai.
Session Layer
Pehle 3 layers (physical, data link, aur network) jo services deti hain, wo kuch processes ke liye kaafi nahi hoti. Session layer network ka dialog controller hoti hai. Ye communicating systems ke beech interaction establish, maintain, aur synchronize karti hai.
Session layer ki kuch khas responsibilities hain:
Dialog control: Session layer do systems ko ek dialog mein aane deti hai. Ye communication do processes ke beech half-duplex (ek taraf se ek waqt mein) ya full-duplex (dono taraf se ek saath) mode mein hone deti hai.
Synchronization: Session layer ek process ko data stream mein checkpoints ya synchronization points add karne ka option deti hai.
Presentation Layer
Presentation layer do systems ke beech exchange hone wali information ke syntax aur semantics se related hoti hai.
Translation: Alag-alag computers alag encoding systems use karte hain. Presentation layer in different encoding methods ke beech interoperability ke liye responsible hoti hai. Sender ki presentation layer information ko uske sender-specific format se ek common format mein convert karti hai. Receiving machine ki presentation layer is common format ko receiver-specific format mein badal deti hai.
Encryption: Sensitive information ko securely bhejne ke liye system ko privacy ensure karni hoti hai. Encryption ka matlab hai ki sender original information ko ek alag form mein badal deta hai aur network par ye encrypted message bhejta hai. Receiver is process ko reverse karke original message wapas hasil karta hai, jise decryption kehte hain.
Compression: Data compression se information ke bits ki sankhya kam ho jati hai. Ye multimedia transmission jaise text, audio, aur video ke liye bahut important hota hai.
Application Layer
Application layer user (chahe human ho ya software) ko network access dene ka kaam karti hai. Ye user interfaces provide karti hai aur electronic mail, remote file access aur transfer, shared database management, aur doosre distributed information services jaise services support karti hai.
Application layer ke kuch specific services hain:
Network Virtual Terminal: Ye ek software version hota hai physical terminal ka, jo user ko remote host pe login karne deta hai.
File Transfer, Access, and Management: Ye application user ko remote host ke files ko access karne (read ya modify karne), remote computer se files local computer pe retrieve karne, aur remote computer ke files ko local computer se manage karne ki facility deti hai.
Mail Services: Ye application e-mail forwarding aur storage ka base provide karti hai.
Directory Services: Ye distributed database sources aur access provide karti hai jisme global information hoti hai alag-alag objects aur services ke baare mein.
Communication Protocols
Sabhi devices ke beech communication tabhi possible hoti hai jab devices data ke format pe agree karte hain. Rules ka ek set jo data ke format ko define karta hai, use protocol kehte hain. Kam se kam, ek communication protocol ko yeh cheeze define karni zaroori hoti hain:
Transmission ki speed (baud ya bps mein)
Transmission synchronous hoga ya asynchronous
Data transmission half-duplex mode mein hoga ya full-duplex mode mein
Iske alawa, protocols sophisticated techniques bhi include kar sakte hain jaise transmission errors ko detect karna aur recover karna, data ko encode aur decode karna.
Centralized vs Decentralized System
Distributed System
Distributed system ek aise independent computers ka group hota hai jo users ko ek single system ki tarah dikhai deta hai. Isme multiple autonomous computers hote hain, jinke apne private memory hote hain, aur ye ek computer network ke through communicate karte hain. Distributed system mein information exchange message passing ke zariye hota hai.
Examples:
World Wide Web (WWW) sabse bada distributed system ka example hai
Internet
Intranet (jo internet ka ek hissa hota hai aur kisi organization ke dwara manage kiya jata hai)
Branch office computers ka network
Distributed Systems ke Centralized Systems par Advantages:
Economics: Microprocessors ka collection mainframes ke comparison mein better price/performance deta hai. Ye cost effective tareeka hai computing power badhane ka.
Speed: Distributed system ke paas total computing power mainframe se zyada ho sakti hai. Jaise 10,000 CPU chips, har ek 50 MIPS pe chal raha ho. Itna powerful single processor banana possible nahi. Load distributing se performance better hoti hai.
Inherent Distribution: Kuch applications khud hi distributed hoti hain, jaise supermarket chain.
Reliability: Agar ek machine crash kar jaye, tab bhi poora system chal sakta hai. Isse availability aur reliability badhti hai.
Incremental Growth: Computing power chhote-chhote hisso mein add ki ja sakti hai. Modular expansion possible hai.
Collaborative Need: Personal computers ki badhti hui sankhya, logon ko collaborate aur information share karne ki zarurat.
Open System: Sabse important aur khas baat distributed system ki ye hai ki ye ek open system hota hai. Matlab ye hamesha ready hota hai doosre systems ke saath communicate karne ke liye. Ek open system jo scale karta hai, wo closed aur self-contained system se better hota hai.
