OWASP Mobile Top 10
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
| ID | Name | Explanation | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|---|
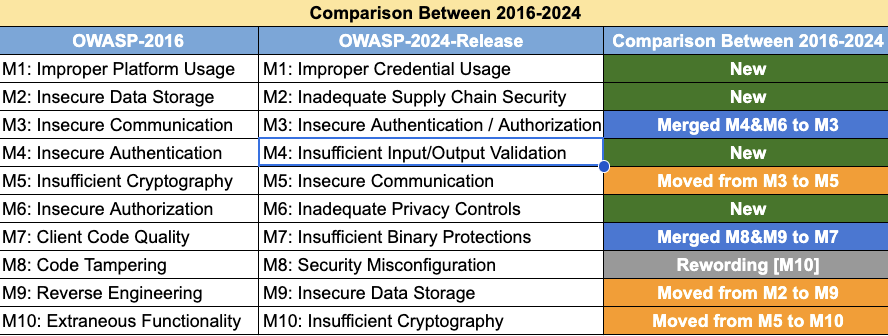
| M1 | Improper Credential Usage | Jab app ke andar hardcoded credentials (jaise API keys, passwords) use ki jaati hain ya baar-baar wahi credentials use hote hain. | Ek banking app ke APK file mein API key hardcoded thi, jis se attackers ne unauthorized access le liya. |
| M2 | Inadequate Supply Chain Security | Jab third-party libraries ya SDKs bina verify kiye use ki jaate hain aur unmein malicious code hota hai. | 2020 mein ek SDK mila jo Android apps ke through bina bataye users ka data collect kar raha tha. |
| M3 | Insecure Authentication/Authorization | Jab login ya access control ka system weak hota hai, jise attacker easily bypass kar leta hai. | Ek app mein login API ko intercept karke doosre users ke data tak access mil gaya. |
| M4 | Insufficient Input/Output Validation | Jab user input ko sahi tareeke se check nahi kiya jaata, jisse injection attacks jaise SQL injection ka risk hota hai. | Ek form field mein SQL injection se pura database dump kiya gaya. |
| M5 | Insecure Communication | Jab app data ko encrypt kiye bina (jaise HTTP) bhejti hai, to attacker easily sniff kar sakta hai. | Ek app ne username-password ko HTTP ke through bheja, jo MITM attack mein capture ho gaya. |
| M6 | Inadequate Privacy Controls | Jab user ka personal data unki permission ke bina collect ya share kiya jaata hai. | Ek fitness app ne GPS location third-party advertisers ko bina user consent ke share ki. |
| M7 | Insufficient Binary Protections | Jab app ke APK mein proper protection (like obfuscation, anti-debugging) nahi hoti, to attacker usse reverse engineer kar sakta hai. | Ek app ko reverse engineer karke in-app purchase ko free kar diya gaya. |
| M8 | Security Misconfiguration | Jab app ya server ka config galat hota hai, jaise debug mode on rehna ya public access enabled hona. | Ek app ka linked cloud bucket public tha, jisme sensitive documents mil gaye. |
| M9 | Insecure Data Storage | Jab sensitive data (jaise passwords, credit card info) device pe bina encryption ke store hoti hai. | Ek ride-sharing app ne user ke card details SQLite DB mein bina encryption ke store kiye, jo rooted device pe dikhe. |
| M10 | Insufficient Cryptography | Jab app weak encryption (jaise MD5) use karta hai ya cryptography ka sahi implementation nahi hota. | Ek messaging app ne passwords ko MD5 se hash kiya tha, jo rainbow tables se easily crack ho gaya. |
OWASP Top 10 Mobile Risks – 2016
| ID | Name | Explanation | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | Improper Platform Usage | Jab app platform-specific security features (jaise Android permissions, Keychain, intents) ko galat tarike se implement karti hai ya ignore karti hai. | Ek app ne Android ke intent filters ka galat use kiya, jisse doosre apps ne sensitive actions trigger kiye. |
| M2 | Insecure Data Storage | Jab sensitive data (jaise passwords, tokens) device pe insecure jagah (shared prefs, SQLite DB) mein store hoti hai bina encryption ke. | Ek health app ne user health data ko plain text mein store kiya jo rooted device se easily access ho gaya. |
| M3 | Insecure Communication | Jab app aur server ke beech ka data encrypted nahi hota ya weak encryption hoti hai. | Ek app ne login info ko HTTPS ke bajaye HTTP se bheja, attacker ne data intercept kar liya (MITM attack). |
| M4 | Insecure Authentication | Jab app ka login/authentication system weak hota hai, jise attacker easily bypass kar sakta hai. | Ek app ne token validation ache se implement nahi kiya, kisi ka bhi token daal ke login ho gaya. |
| M5 | Insufficient Cryptography | Jab app weak ya khud ka bana hua encryption use karti hai jo easily break ho sakta hai. | Ek messaging app ne messages ko base64 “encode” kiya instead of real encryption—easy to decode. |
| M6 | Insecure Authorization | Jab app proper access control nahi lagati aur attacker unauthorized actions perform kar sakta hai. | Ek e-commerce app ne order cancel karne ke API mein user check nahi kiya, koi bhi order cancel ho gaya. |
| M7 | Client Code Quality | Jab app ke code mein logic bugs ya insecure coding practices (jaise unchecked inputs) hote hain. | Ek app crash ho gaya jab attacker ne unexpected input diya, jisse DoS attack hua. |
| M8 | Code Tampering | Jab app ko modify (tamper) kiya ja sakta hai, jaise in-app purchases ko bypass karna. | Ek gaming app ko modify karke unlimited coins mil gaye—app ne integrity check nahi kiya. |
| M9 | Reverse Engineering | Jab app ka APK easily reverse engineer kiya ja sakta hai to steal logic, API keys, ya sensitive info. | Ek attacker ne app ka source code decompile karke API keys aur hidden features nikaal liye. |
| M10 | Extraneous Functionality | Jab app mein aise hidden/debug functions rehte hain jo production version mein nahi hone chahiye. | Ek app mein developer debug panel active tha, jisse attacker ne internal APIs ka access le liya. |
OWASP Top 10 Mobile Risks – 2014
| ID | Name | Explanation | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | Weak Server Side Controls | Jab backend server pe proper security (jaise authentication, input validation, rate limiting) nahi hoti, to attacker backend ko exploit kar sakta hai. | Ek app ka backend API bina authentication ke public tha, jisse attacker ne sab users ka data access kar liya. |
| M2 | Insecure Data Storage | Jab sensitive data (passwords, tokens) device pe insecure tareeke se store hoti hai, jaise bina encryption ke. | Ek app ne session token ko plain text mein store kiya, jo rooted phone se easily mil gaya. |
| M3 | Insufficient Transport Layer Protection | Jab data app aur server ke beech properly encrypt nahi hota, jaise HTTPS ka use na karna ya certificate pinning na hona. | Ek shopping app ne payment data HTTP ke through bheja, jisse MITM attacker ne data sniff kar liya. |
| M4 | Unintended Data Leakage | Jab app background mein ya third-party libraries ke through user data leak karti hai bina user ke pata chale. | Ek wallpaper app ne user contact list analytics SDK ke through third-party ko bhej di. |
| M5 | Poor Authorization and Authentication | Jab login ya authorization mechanism weak hota hai, jise attacker bypass karke unauthorized access le sakta hai. | Ek app ne session tokens ko expire nahi kiya, kisi bhi purane token se login ho jata tha. |
| M6 | Broken Cryptography | Jab encryption algorithms ya implementation hi kharab hoti hai—jaise weak algorithms (MD5), khud se banaye hue encryption, ya key exposure. | Ek app ne messages ko encrypt kiya par key hardcoded thi, attacker ne key nikaal ke messages decrypt kar liye. |
| M7 | Client Side Injection | Jab attacker client side par malicious input dekar code inject karta hai—jaise JavaScript ya SQL. | Ek app ne user input ko bina sanitize kiye HTML page mein dikhaya, jisse attacker ne XSS payload inject kiya. |
| M8 | Security Decisions Via Untrusted Inputs | Jab app trust kar leti hai user input pe bina verify kiye aur security ka decision leti hai. | Ek app ne debug mode user ke input se enable hone diya, attacker ne request modify karke debug access le liya. |
| M9 | Improper Session Handling | Jab session tokens ko securely handle nahi kiya jaata—jaise expire na karna, predictability, ya secure flag ka na hona. | Ek app ne logout ke baad bhi session active rakha, jisse token reuse karke access liya gaya. |
| M10 | Lack of Binary Protections | Jab app reverse engineering se bachane ke liye obfuscation, anti-debugging, ya tamper detection nahi lagati. | Ek attacker ne app decompile karke API keys nikaal li aur fake app bana diya. |
